The rapid rise of ChatGPT has ignited a race to adopt smarter and more powerful AI models across the enterprise.
Companies are increasingly exploring what are coming to be known as "AI copilots" to boost efficiency and performance across various tasks. With the continuous advancement of these copilots, businesses must have a clear strategy in place to capitalize on their potential.
We introduced a four-tier AI copilot framework during our Moveworks Live event to clarify what you should consider when implementing an AI copilot solution in your business and what tech investment level you’ll need to make to successfully achieve your goals.
Today, I’ll dive into this framework to help you determine your copilot strategy, answering questions such as:
- What is an AI copilot?
- What does it take to build a copilot-like experience into your business?
- What is the four-tiered AI copilot strategy framework?
>> Learn how to build an AI copilot strategy that works for you. Download the enterprise copilot handbook!
First things first, what is an AI copilot?
An AI copilot is a conversational interface that uses large language models (LLMs) to automate tasks and retrieve information. By leveraging LLMs, copilots understand and respond to human language effectively, making it easier for users to interact with and navigate digital platforms.
Examples of AI copilots
- OpenAI's ChatGPT: A large-scale conversational AI capable of responding to questions, providing recommendations, and helping draft content naturally. ChatGPT can help streamline various high-level tasks and workflows, making it an invaluable partner for navigating everyday challenges.
- Jasper’s copywriting assistant: An AI copilot that aids users in generating on-brand content — from emails to blog posts to web copy. By understanding the user's input and providing relevant suggestions, content creators can save time, increase productivity, and improve the quality of their written material.
- Microsoft's Copilot for Microsoft 365: An AI copilot designed to help users with a range of tasks across the Microsoft ecosystem, including in applications such as Word, Excel, and PowerPoint through automated text and layout suggestions, email summaries, and real-time assistance during meetings.
- Salesforce’s Einstein GPT: An AI copilot that generates personalized content across every Salesforce instance, enhancing employee productivity. Open and extensible, it supports both public and private AI models so that Salesforce customers can elevate CRM efficiency with out-of-the-box generative AI.
- Github’s Copilot: An AI-driven code completion copilot which helps developers write code more efficiently by suggesting entire lines or blocks of code. By learning from the context and past code in a repository, Github Copilot offers tailored recommendations, reducing development time and making the coding process more intuitive.
- Moveworks’ Enterprise AI Assistant: An AI copilot that helps employees automate tasks and access information across all enterprise applications using a single natural language interface. It supports a multitude of functions, such as password resets, PTO requests, or expense submissions, and ensures seamless support for all employees, regardless of their language or preferred communication channel.
As AI continues to develop rapidly, copilots will play an increasingly vital role in helping users streamline their tasks and better use their digital resources. In light of this, defining a well-structured copilot strategy becomes essential for businesses aiming to harness the full potential of AI technology.
What does it take to build a copilot-like experience into your enterprise?
Before developing an AI copilot strategy, you need to understand what it takes to build a copilot-like experience into your enterprise. There is a vast difference between ChatGPT and an enterprise copilot platform that is fully integrated within an organization. This is not to say that ChatGPT isn’t helpful. It is incredibly helpful for certain use cases. But it’s limited in its ability.
For a copilot to own more enterprise-focused tasks, you need a less general, more tailored approach that can manage:
- Domain-specific requirements: Understanding the unique needs, challenges, and objectives of each department involved in the copilot is crucial. That includes a wide range of enterprise service needs — identity, permissions, security, compliance, and more.
- Relevant data inputs: The key to building a copilot is to gather and process relevant data specific to each domain. This requires a team of annotators to provide tags, descriptions, ratings, translations, and well-researched examples so the copilot can provide the best possible support.
- System integrations: Connect the copilot to the right tools, technologies, and systems for each department, ensuring seamless collaboration across domain-specific applications.
- Custom AI models: Fine-tune the LLMs according to domain-specific data sources, desired outcomes, and unique challenges specific to each domain for more accurate decision-making.
- Strong analytics and data science team: Staff with expertise in data analysis and machine learning development are required to support the copilot's learning and optimization and ensure that the experience improves over time instead of degrading.
- Consistent, intuitive user experience: To maintain a straightforward and seamless interaction with the copilot, you need a conversational AI system that lets users easily take full advantage of its capabilities.
- Robust security infrastructure: Especially for an enterprise copilot, engaging with security experts to safeguard sensitive enterprise data, protect user privacy, and adhere to necessary compliance measures is mandatory.
Given the above, it should be clear that incorporating a copilot experience into your organization takes considerable effort. While some use cases might be lighter lifts, others will require heavy, long-term maintenance. The scope of the problem you’re trying to solve will require varying degrees of investment. For example, using AI to provide enterprise-wide support will, by definition, need a much better understanding of and investment in the bullets above than using AI to write web copy.
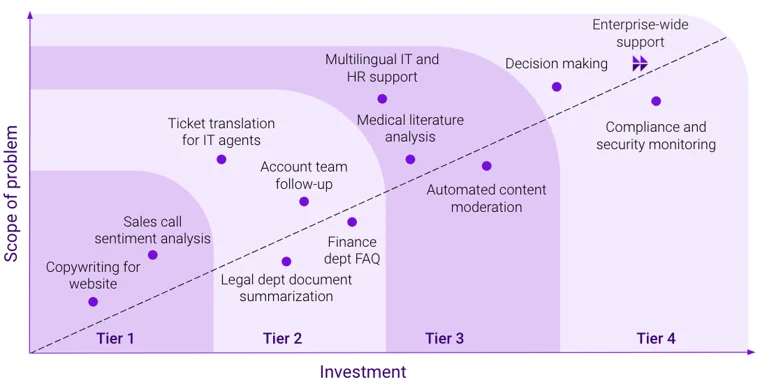 Figure 1: When looking at AI copilot use cases, we start to see the relationship between the scope of the problem and the investment required to solve it, enabling decision-makers to make informed choices when embracing LLMs for their organizations.
Figure 1: When looking at AI copilot use cases, we start to see the relationship between the scope of the problem and the investment required to solve it, enabling decision-makers to make informed choices when embracing LLMs for their organizations.
This is to say that an AI copilot is not something you can build and maintain on your own, particularly if you want to expand its functionality across the enterprise. Investing in the right partner with the right resources is the key to successfully implementing a helpful and efficient AI copilot.
The four-tiered AI copilot strategy framework
We created a four-tiered framework to help leaders better understand the technology and investments necessary to integrate LLMs into production environments.
By grasping the nuances between various AI copilots and their unique capabilities and limitations, you will be better equipped to create a compelling and tailored strategy for your organization.
Tier-one copilot: Basic LLM integration
A tier-one copilot involves a basic API call of a large language model (LLM). In this approach, prompt engineering is used to help a user access general information, and the copilot is primarily aimed at improving efficiency across high-level use cases.
Tier-one copilot use case examples
A tier-one copilot simplifies various everyday tasks by leveraging AI-powered assistance. Some common use cases include:
- Generating content suggestions for social media posts
- Auto-completing email drafts or responses
- Providing answers to frequently asked questions
- Summarizing general content
- Identifying and fixing grammar and style errors
- Performing sentiment analysis on sales call transcripts
 Figure 2: Tier-one copilots rely on basic LLM integrations to solve small-scale enterprise challenges.
Figure 2: Tier-one copilots rely on basic LLM integrations to solve small-scale enterprise challenges.
What you need to get started with a tier-one copilot
Tier-one copilots are relatively easy to kick off, requiring minimal resources and offering a low barrier to entry, making them an attractive starting point for organizations exploring AI tools.
Launching the copilot boils down to accessing an LLM, such as GPT-4. LLM-as-a-service providers, like Hugging Face and OpenAI, make this process even more accessible. You simply subscribe to a reliable API provider for your chosen LLM and integrate their API into your software or platform. This streamlined approach needs little beyond developer resources dedicated to implementing the API integration, ensuring a smooth and cost-effective way to introduce AI-driven assistance into your organization.
Key machine learning technique: Prompt engineering
Prompt engineering is a crucial machine learning technique that bolsters the effectiveness of tier-one copilots.
By thoughtfully crafting and refining user prompts based on previous interactions, you can elicit more accurate model responses that better align with users' needs. While prompt engineering is more art than science, advanced tactics such as auto-prompting and prompt tuning can significantly enhance your tier-one copilot's performance, taking it one step closer to the desired outcome.
Strengths of the tier-one copilot
- Rapid deployment with a low upfront cost: With quick implementations that involve minimal developer resources and low entry barriers, tier-one copilots are an ideal starting point for organizations venturing into AI-driven assistance.
- Access to general AI capabilities: Generating content via a conversational interface streamlines and enhances user interactions across common use cases.
- Basic customization: Slight adjustments can be made to the copilot's behavior to suit the specific needs of a business while still maintaining its general functionality and versatility.
Limitations of the tier-one copilot
- Limited domain and organizational specificity: Their effectiveness is primarily confined to the given use cases, with limited scope for more complex or specialized tasks.
- Potential for hallucinations: Tier-one copilots may exhibit lower accuracy in domain-specific tasks, as they are not customized for each unique industry or field.
- API costs can become expensive based on usage: The success of a tier-one copilot relies on third-party API providers for LLM access and support, which could result in increased operational expenses as usage scales.
- Security and privacy worries: Entrusting sensitive information to a third-party service can raise concerns regarding data confidentiality and compliance with industry-specific regulations.
Tier-two copilot: Customized LLM implementation
A tier-two copilot is a customized implementation of an LLM fine-tuned and grounded with an organization's domain-specific data. Unlike off-the-shelf models trained on general internet data, tier-two copilots are designed to perform tasks and generate answers that cater to specialized areas.
Tier-two copilot use case examples
A tier-two copilot is better prepared to manage some domain-specific tasks. Some common use cases include:
- Translating IT support tickets
- Drafting an FAQ for the Finance department
- Summarizing legal documents
- Generating industry-specific content for marketing materials
- Assisting with medical diagnosis based on patient symptoms and medical history
- Identifying trends in customer feedback data and providing actionable insights
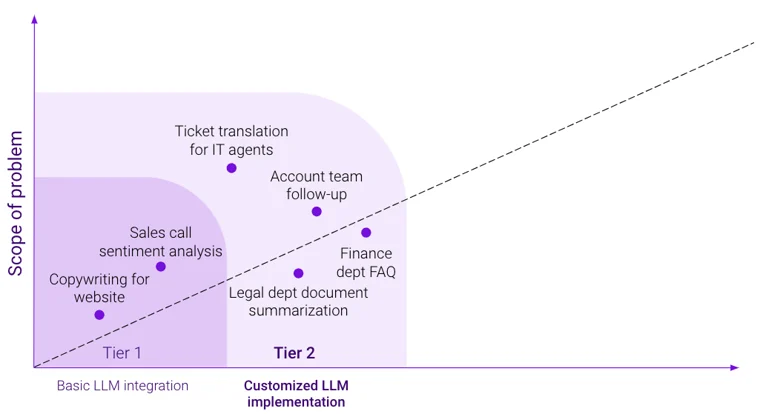 Figure 3: Tier-two copilots offer more customized LLM implementations.
Figure 3: Tier-two copilots offer more customized LLM implementations.
What you need to get started with a tier-two copilot
Developing a tier-two copilot involves a substantial upfront investment in resources and expertise. Key elements include pre-trained models, supporting infrastructure such as GPUs, and a skilled team of developers and machine learning engineers capable of selecting a suitable pre-trained model, like LLaMA, RoBERTa, MPNet, or Flan-T5, and fine-tuning it with the organization's domain data for a more customized LLM implementation.
Annotation is also critical for this more focused approach. And while the annotation process can commence with external service providers like Scale.ai, it’s essential to transition in-house as you advance to higher tiers with increased domain specificity and scrutiny.
Although tier-two copilots demand more resources and investment than their tier-one counterparts, the payoff is a high-performance, domain-specific AI solution that tackles your organization's unique challenges.
Key machine learning techniques: Fine-tuning, grounding, retrieval augmentation
Optimizing the performance of an AI-driven copilot necessitates leveraging key machine learning techniques such as fine-tuning, grounding, and retrieval augmentation.
Fine-tuning involves adapting the chosen base model to a specific task using labeled, domain-specific data. Then, both grounding and retrieval augmentation can enhance the copilot's factuality and accuracy by utilizing contextual information from user data, unique entities, query patterns, and curated documents.
These techniques work in harmony to deliver tailored AI-driven assistance that caters to an organization's unique needs and challenges, providing highly relevant, meaningful, and contextually accurate results.
Strengths of the tier-two copilot
- Enhanced domain-specific performance: The tier-two copilot's customization, fine-tuning, and domain-specific learning improve accuracy and effectiveness within a specific industry or field.
- Reduced security and privacy risks: Transitioning from third-party APIs to an in-house solution lead to better control of sensitive data, addressing safety concerns and compliance with industry-specific regulations.
- Potential cost savings over API usage: Although the initial investment may be higher, developing a tier-two copilot can lead to long-term savings by eliminating dependency on third-party API providers and minimizing usage costs.
- Lowered risk of hallucination: Specialized training, grounding, and retrieval augmentation techniques can reduce the chance of inaccurate responses or hallucinations, ensuring more reliable AI assistance.
Limitations of the tier-two copilot
- Limited to single-step use cases: Tier-two copilots are primarily designed to handle tasks that involve singular, discrete actions. As such, they may not be suitable for managing complex, multi-step processes or facilitating comprehensive workflow solutions.
- Limited actionability for each use case: As tier-two copilots only offer basic support for individual use cases, their ability to deliver actionable insights or automate next steps is limited.
- Limited performance and control with a single LLM: With a tier-two copilot, organizations only have access to one language model, which may result in poor performance for certain tasks that require more advanced reasoning, contextual understanding, or domain-specific expertise.
- Risk of missing or stale data: Tier-two copilots may face challenges in staying up-to-date with the latest information and trends, potentially leading to decision-making based on stale or incomplete data. This limitation further underscores the need for ongoing monitoring and maintenance to ensure the efficacy of the copilot.
Tier-three copilot: Advanced LLM pipelines
A tier-three copilot involves chaining multiple LLMs together, creating sophisticated pipelines optimized for multi-step use cases that leverage the strengths and capabilities of each LLM involved. As a result, the tier-three copilot can provide tailored assistance and solutions for intricate domain-specific challenges.
Tier-three copilot use case examples
By incorporating multiple LLMs and advanced techniques, tier-three copilots can tackle a broader range of use cases, enhance productivity and efficiency, and address challenges in more sophisticated domains. Some common use cases include:
- Analyzing medical literature
- Automating account team follow-up
- Providing multilingual IT and HR support
- Moderating content
- Assisting in the creation and evaluation of financial models and projections
- Analyzing and optimizing supply chain operations for businesses
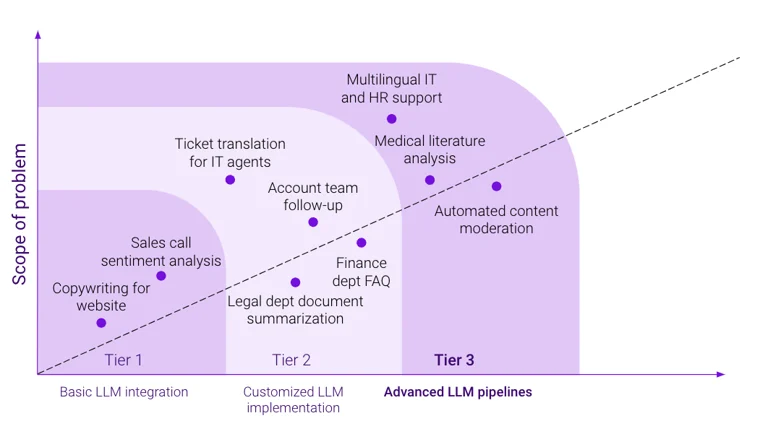 Figure 4: Tier-three copilots bring together multiple LLMs to manage complex use cases.
Figure 4: Tier-three copilots bring together multiple LLMs to manage complex use cases.
What you need to get started with a tier-three copilot
To get started with a tier-three copilot, there are several key elements and investments you need to consider. First, you must create a multi-LLM stack consisting of various pre-trained models designed to work together for more complex tasks. It is essential to have connectors in place to enable seamless system integrations and facilitate the interactions between different LLMs.
As is also the case with tier-two copilots, investing in fine-tuning is crucial for optimizing the models in the multi-LLM stack. Along with this, system integrations help the copilot assimilate into your organization's existing workflows and automation.
Allocating resources for annotators to generate high-quality domain-specific data will ensure improved performance for your copilot. Likewise, assembling dedicated AI and machine learning teams is vital for developing, implementing, and optimizing the tier-three copilot.
Key machine learning techniques: Chaining, entity extraction and linking, connectors
Developing a robust tier-three copilot capable of tackling complex, multi-step tasks involves several advanced machine learning techniques.
First, chaining allows for the seamless integration of multiple LLMs in a pipeline, tapping into the combined strengths of each model for superior performance. This is further complemented by entity extraction and linking, which enable the identification and correlation of crucial data points within the input context, providing richer layers of information for the copilot.
Connectors also play a vital role as intermediaries between the LLM stack and existing systems, facilitating efficient communication and enhancing the overall coherence of the AI-driven solution. By incorporating these sophisticated techniques, tier-three copilots can effectively address intricate use cases, driving productivity and efficiency within an organization.
Strengths of the tier-three copilot
- High control and performance: By tapping into the unique strengths of each LLM, tier-three copilots can generate more accurate, contextually aware, and actionable insights across diverse scenarios, meeting the demands of complex problem-solving within organizations.
- More actions involving existing systems: These copilots can be effectively integrated with current systems in the organization, allowing for seamless execution of additional actions and support within the established infrastructure.
Limitations of the tier-three copilot
- Challenging to scale for enterprise-wide business problems: Tier-three copilots, while excelling in complex tasks, may encounter difficulties when attempting to scale for larger, enterprise-wide issues that require a more comprehensive approach and broader LLM coverage.
- Risk of cognitive overload for users: As tier-three copilots employ advanced techniques and multi-step actions, users may be overwhelmed by the increased complexity and multitude of interactions within the AI-driven solution.
Tier-four copilot: Enterprise-wide LLM adoption
Tier-four copilots work to address the challenges inherent in providing extensible employee support and facilitating autonomous decision-making.
As a sophisticated LLM system specifically designed for enterprise-wide deployment, these tier-four copilots encompass advanced features like a reasoning engine, analytics, security, and privacy, as well as out-of-the-box connectors catering to the demanding requirements of large organizations.
Tier-four copilot use case examples
A tier-four copilot can handle issues across multiple functions, channels, languages, and departments. Here are just a handful of examples:
- Providing enterprise-wide support
- Assisting with decision-making by providing insights, predictions, and recommendations
- Monitoring compliance and security
- Managing intellectual property
- Uplevelling customer service and engagement
- Curating and generating content across an organization
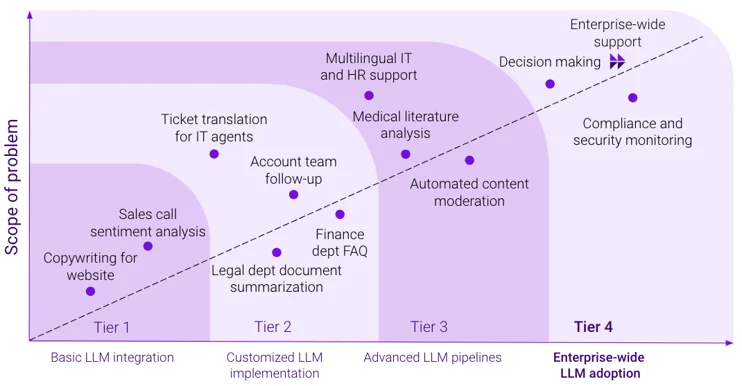 Figure 5: Tier-four copilots are specifically designed for enterprise-wide deployment.
Figure 5: Tier-four copilots are specifically designed for enterprise-wide deployment.
What you need to get started with a tier-four copilot
Accuracy and factuality are of paramount importance when incorporating a tier-four copilot in enterprise settings such as legal, corporate development, or finance departments. Organizations must invest in multiple specialized teams to effectively implement a tier-four copilot, including design, UX, annotation, machine learning, systems integration, and security compliance and privacy infrastructure.
Advanced reasoning techniques further enhance the performance of a tier-four copilot, enabling it to tackle complex problems and improve employee productivity. Organizations can leverage robust language models to optimize their decision-making processes and streamline operations across departments by grounding the copilot to specific use cases.
Key machine learning technique: Reasoning, deep integrations
As organizations increasingly rely on language models, powerful decision-making and reasoning capabilities have become indispensable. As mentioned, generalized LLMs struggle to navigate complex challenges as more use cases, systems, and teams are added. Tier-four copilots, with chained models explicitly designed for decision-making and reasoning, are essential to bridge this gap.
However, as use cases expand, managing and scaling these models without compromising performance is a complex task for machine learning engineers and data scientists. Models must be agile, delivering accurate results even as they evolve.
The rapid growth in system complexity and ever-changing use cases requires deep integrations in systems across the enterprise. Tier-four copilots must be adept at scaling quickly and adapting to new environments. These integrations allow for improved information flow across various systems in an organization for better reasoning capabilities.
Strengths of the tier-four copilot
- End-to-end control: If something isn’t working in an enterprise environment, you must know why. Tier-four copilots enable organizations to effectively identify new use cases, allocate resources, and implement changes promptly. As organizations expand their user journeys and data complexity grows, tier-four copilots skillfully handle various data types and volumes, ensuring streamlined control and adaptability to evolving requirements.
- Strong security and compliance: As tier-four copilots extend to various departments, including Legal and Security, robust data protection measures become paramount. These copilots clearly separate proprietary information across different departments and enable strictly controlled access and permissions. By implementing and maintaining a multitude of security structures, tier-four copilots provide a reliable, compliant solution suitable for sensitive data handling.
- Coverage across a variety of use cases: Tier-four copilots support a wide range of use cases across diverse enterprise environments. Their adaptable nature, coupled with advanced reasoning capabilities, allows organizations to use them in various departments and scenarios. This flexibility ensures that tier-four copilots can handle unique challenges, streamline operations, and contribute to greater organizational efficiency and productivity.
What makes Moveworks a tier-four copilot?
Moveworks sets itself apart as a tier-four copilot by both harnessing hundreds of machine learning models, specifically fine-tuned to enterprise data, and deeply integrating with the organization’s disparate tech stack to fully connect the enterprise ecosystem.
By partnering with Moveworks, organizations can access accurate, verifiable information through controlled outputs that leverage proprietary data for precision and relevance.
Extensibility is at the heart of Moveworks, enabling users to expand the copilot into new domains and use cases. The recently launched Creator Studio embodies this concept, providing the Moveworks copilot with extraordinary capabilities tailored to the needs of growing enterprises.
Our commitment to retaining task-level precision is critical for delivering a high level of service and addressing complex enterprise challenges. And our domain expertise, extensibility, and customization position us as a leading tier-four copilot, empowering organizations to leverage advanced language models to improve efficiency, accuracy, and innovation in today's competitive business landscape.
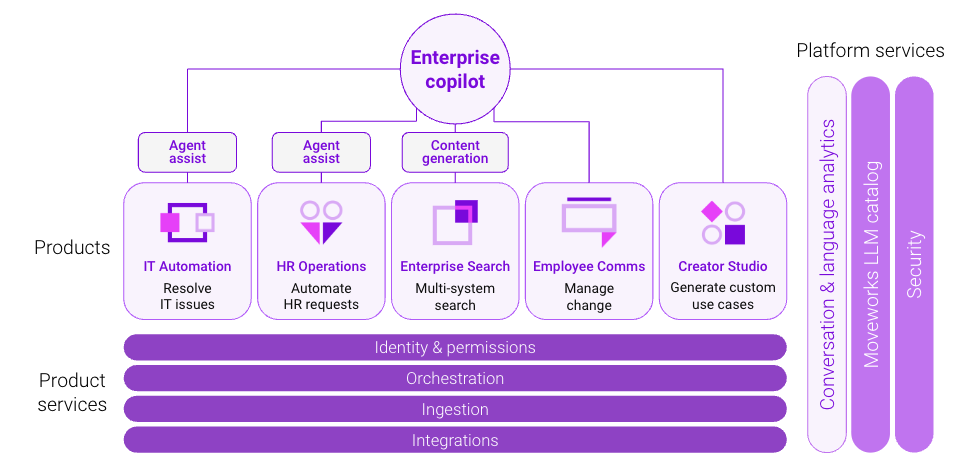 Figure 6: The Moveworks enterprise copilot platform integrates with every business system, meaning it can support any use case across any department.
Figure 6: The Moveworks enterprise copilot platform integrates with every business system, meaning it can support any use case across any department.
Find the right AI copilot strategy for your enterprise
It goes without saying that now is an exciting time to build using large language models. We’re at the beginning of a massive enterprise transformation driven by new AI tools like copilots. And as businesses adopt these cutting-edge solutions, having a well-defined copilot strategy is paramount to success.
Throughout this article, we've explored our four-tier AI copilot framework to help you better understand the investment levels and implementation considerations when integrating AI copilots into your business. By assessing your organization's unique requirements and goals, you can align the appropriate copilot tier to maximize the benefits of these advanced AI models.
In an ever-evolving business environment, staying ahead of the curve is vital. A deep understanding of AI copilots and a commitment to developing an effective strategy will propel your organization to new heights. It’s time to seize the opportunities offered by this technology and empower your people with innovative AI copilot solutions.
See the rest of Moveworks Live. Check it out!
Table of contents



